Complete Guide to Internet Speed 2024

HighSpeedOptions prides itself on providing honest, quality content. While we may be compensated when you make a purchase through links on our site, all opinions are our own. Here's how we make money.
Table of Contents
With dozens of features to choose from, it can be quite difficult to select an internet plan that fits your lifestyle. That’s where our Complete Guide to Internet Speed comes in. Packed with everything you need to know about internet speed, our easy-to-follow guide will help you understand your connection better and teach you how to make it work faster for you.

What is Internet Speed?
Think of internet speed like highway traffic: it all comes down to how much volume can travel at any given time before reaching a stopping point. Similar to cars on a highway with a limited number of lanes, the amount of data transferred between your connected devices and the internet at a particular time is dependent on how much bandwidth you pay for.
Unless you upgrade your internet plan to include more speed, you’re limited to a certain threshold. If your internet speed is too slow, you might have trouble performing daily activities like browsing the internet, online gaming, streaming videos, or working remotely. If it’s too fast, you could be overpaying for internet speed you don’t need.
Internet providers advertise their network’s fastest possible speeds, so don’t be surprised if your speed test varies slightly day-to-day. Your internet experience mainly depends on a variety of factors outside your provider’s control. The most common explanation is your connection type.
Connection Types
There are five basic types of internet connections to choose from: fiber, cable, DSL, satellite, and fixed-wireless.
Fiber Internet
The latest in internet technology, fiber internet uses light rather than electric signals to transfer data along fiber-optic glass cables. It offers the fastest speeds, delivers the largest home coverage, and supports the most device connectivity among connection types. However, since it’s not as widely available as DSL and cable internet, it makes up only 1 in 5 internet subscribers nationwide.
- Fastest download and upload speeds
- Most reliable connection
- Supports the most connected devices
- High price tag
- Limited availability in the U.S.
- Slow overbuild process
Cable Internet
Similar to DSL, cable internet uses electrical signals to establish an internet connection from a provider to a home. But, instead of passing that signal through copper phone lines, cable internet runs on the same coaxial cables as your TV service and is usually more reliable than DSL. Its faster speeds and accessibility make it the leading internet connection today, with 3 in 5 (63%) current internet subscribers nationwide.
- 3x the availability than fiber
- Supports heavy usage like gaming and streaming
- High internet speeds
- Slower speeds during peak hours
- Limited availability in rural areas
- Moderate to high prices
DSL Internet
A digital subscriber line (DSL) is one of the most common connections in the United States due to its availability. It uses pre-existing copper phone lines to transmit internet signals to your home. DSL internet is a step up from dial-up service but is still known to cause dead spots, latency issues, and all-around slower speeds compared to cable and fiber.
- Most affordable connection
- 3x the availability than fiber
- Faster than dial-up
- Slow to Average speeds
- Doesn’t support gaming or streaming well
- Weak home coverage
Satellite Internet
Satellite internet is a wireless connection that utilizes satellite technology to transmit internet signals among 3 satellite dishes. One is set up at your provider’s main hub, one is set up on your property, and one is in space. This connection type has the unique advantage of being available virtually anywhere, but it is subject to unreliability due to bad weather or equipment.
- Available virtually everywhere
- Can overcome physical barriers
- Faster than dial-up
- Typically expensive
- Data caps are common
- Unreliability due to physical elements
Fixed-Wireless Internet
This type of connection uses cell towers to transmit internet signals over radio waves. It’s most common in rural areas where hard-wired cable connections are difficult to lay, yet is limited by line of sight requirements due to the way it transmits a signal. Fixed-wireless internet is only recommended for households with minimum internet usage.
- Delivers internet to underserved areas
- Easy installation
- Local customer service
- Line of sight limitation
- Slow speeds
- Can be expensive
Difference Between Internet and WiFi
The terms “internet” and “WiFi” are frequently used interchangeably to describe having access to the web. But make no mistake: internet and WiFi are two completely different things. They may interact together like cars on a highway, but you can very well have one without the other and still access your favorite sites.
Internet refers to the overall infrastructure linking millions of computers together from around the world. It allows you to transfer data (information) between devices.
WiFi on the other hand acts as the car that drives on said infrastructure. WiFi enables your devices to connect to the internet and receive data.
You can learn more about the difference between internet and WiFi to help better understand your connection and why you may be experiencing poor service.
Bandwidth vs. Internet Speed
“Bandwidth” and “internet speed” are used interchangeably, but they actually represent two different traits of internet service. While internet speed refers to how fast data is transferred between devices, bandwidth refers to the overall capacity of a particular network.
Say your internet plan advertises speed up to 50 Mbps. That 50 Mbps represents your bandwidth, or network’s top capacity. Your speed would only ever reach 50 Mbps if you were using your bandwidth at full capacity. It’s important to keep this in mind when selecting a plan and testing internet speed on your connection as they are two different things.
Download vs. Upload Speeds
When you choose an internet plan, there are two different types of speed you pay for: download speed and upload speed.
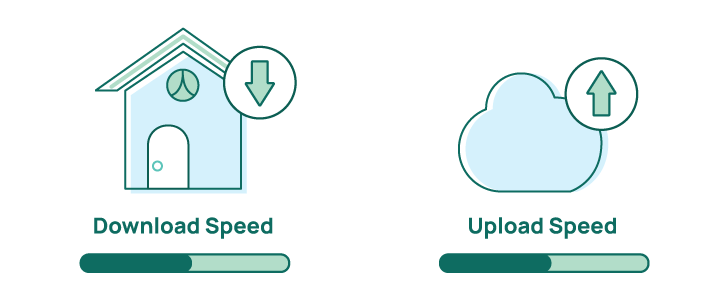
Download speed is how fast information (data) travels from the internet to your connected device. For example, you use download speeds when you stream a Disney+ movie or scroll through your Twitter feed. Internet providers prioritize download over upload speeds, so download speed is used first to advertise service.
Upload speed is how fast information (data) travels from your connected device to the internet. Internet-based activities like uploading a photo to Facebook or sharing a presentation to the cloud for work require upload speed. Since these types of activity are less common, providers normally don’t offer a very high upload speed.
Symmetrical speeds refer to internet plans that offer the same upload and download speeds. This typically costs more than traditional internet packages and is only available with fiber internet.
Data Usage
Data usage is the measurement of how much data is required to perform any given task online. Most internet providers enforce a certain data limit per household to help regulate their network and avoid congestion. However, some providers offer access to unlimited data as a perk or for an additional cost.
Your internet speed needs ultimately depend on your data usage. The FCC recommends a minimum of 25 Mbps for homes with more than one user, however, standard internet packages now start at speeds up to 50 Mbps.
While it’s hard to calculate future usage, here are estimates on data required for different internet-based activities to give you an idea of what speed you need:
General Usage:
| Activity | Data Per Hour | Required Speed |
| Basic Web Browsing | 20 MB | 1 Mbps |
| 50 MB | 1 Mbps | |
| Social Media | 150 MB | 1 Mbps |
| Music Streaming | 150 MB | 0.5 Mbps |
| Activity | Basic Web Browsing |
| Data Per Hour | 20 MB |
| Required Speed | 1 Mbps |
| Activity | |
| Data Per Hour | 50 MB |
| Required Speed | 1 Mbps |
| Activity | Social Media |
| Data Per Hour | 150 MB |
| Required Speed | 1 Mbps |
| Activity | Music Streaming |
| Data Per Hour | 150 MB |
| Required Speed | 0.5 Mbps |
Working:
| Activity | Data Per Hour | Required Speed |
| Telecommuting | 1 GB | 25 Mbps |
| Online Classes | 1 GB | 25 Mbps |
| File Downloading | 2-5 MB | 10 Mbps |
| Activity | Telecommuting |
| Data Per Hour | 1 GB |
| Required Speed | 25 Mbps |
| Activity | Online Classes |
| Data Per Hour | 1 GB |
| Required Speed | 25 Mbps |
| Activity | File Downloading |
| Data Per Hour | 2-5 MB |
| Required Speed | 10 Mbps |
Watching Videos:
| Activity | Data Per Hour | Required Speed |
| SD Video Streaming | 1 GB | 4 Mbps |
| HD Video Streaming | 3 GB | 8 Mbps |
| Ultra HD 4K Video Streaming | 7 GB | 25 Mbps |
| Activity | SD Video Streaming |
| Data Per Hour | 1 GB |
| Required Speed | 4 Mbps |
| Activity | HD Video Streaming |
| Data Per Hour | 3 GB |
| Required Speed | 8 Mbps |
| Activity | Ultra HD 4K Video Streaming |
| Data Per Hour | 7 GB |
| Required Speed | 25 Mbps |
Gaming:
| Activity | Data Per Hour | Required Speed |
| Gaming – Single Player | 40 MB | 3 Mbps |
| Gaming – Multi-Player | 60 MB | 4 Mbps |
| Activity | Gaming â Single Player |
| Data Per Hour | 40 MB |
| Required Speed | 3 Mbps |
| Activity | Gaming â Multi-Player |
| Data Per Hour | 60 MB |
| Required Speed | 4 Mbps |
Video Conferencing:
| Activity | Data Per Hour | Required Speed |
| SD Video Calls | 200 MB | 1 Mbps |
| HD Video Calls | 350 MB | 2 Mbps |
| HD Video Conferences | 1 GB | 6 Mbps |
| Activity | SD Video Calls |
| Data Per Hour | 200 MB |
| Required Speed | 1 Mbps |
| Activity | HD Video Calls |
| Data Per Hour | 350 MB |
| Required Speed | 2 Mbps |
| Activity | HD Video Conferences |
| Data Per Hour | 1 GB |
| Required Speed | 6 Mbps |
Latency
Latency is the time it takes for data to transfer from one computer to your network and back again. Oftentimes, latency is used interchangeably with terms such as ping, ping time, and lag, but they all mean different things.
- Latency is the time it takes for a signal (aka data) to travel from your device to your network and back again.
- Ping refers to a test sent from your computer to test latency (the connection between your devices and the network).
- Ping time is the measure of latency, its unit represented in milliseconds.
- Lag is our experience of latency. The longer time it takes to establish a connection between devices, the greater the lag. This comes in the form of buffering.
Keep in mind the performance of different internet connections when selecting an internet provider for your home. Find out what internet speeds fit your lifestyle and compare options near you before making your final decision.
Internet Speed Test
Since your internet-based activities require a certain amount of speed to work well, we recommend testing your internet connection regularly to see how it performs over time. An internet speed test should tell you your download vs. upload speeds, ping time, and IP address.
Take a speed test to gauge your internet performance. Internet service providers always advertise their network’s fastest speeds, but you should at least be 50 Mbps to 100 Mbps within range of that top speed you’re paying for.
If your speeds are significantly slower than advertised, your speed test could be used to negotiate a better price or free service upgrade.
Reasons for Slow Internet

Contrary to popular belief, your internet service provider generally isn’t the cause for most poor internet experiences. More times than not, your slow internet connection is likely due to one of these issues that’s fairly easy to fix.
*Disclosure: Some of the links below are affiliate links, meaning, at no additional cost to you, HighSpeedOptions will earn a commission if you click and make a purchase.
Equipment Location
The #1 reason for slow internet is equipment location. If your router and/or modem is behind your entertainment system or on the first floor of a multi-story home, you might consider relocating them to a better location. Similar to a lamp, both routers and modems need space of their own to perform at their maximum effectiveness. Things like big furniture or a home layout with thick walls can obstruct the path of your WiFi signal, causing latency and dead spot issues throughout your home. The best location for your internet equipment is away from other chords or large furniture, off the floor, and on the highest level of your home to allow for smoother signal transmission.
Open Network
If you’re running low on bandwidth, it might be because you have an open network. An open network is a network that anyone within signal range can access. This is bad for two reasons: 1) the more devices connected to your network, the less bandwidth available, and 2) your network is left vulnerable to cyber attacks and malware. Both lead to slow internet speed. The quickest solution for this is to create a WiFi password. Then, you can limit the number of devices accessing your personal network, which in turn conserves the bandwidth you pay for. We recommend using a complex series of 8+ upper and lowercase letters, symbols, and numbers for this password and encourage you to update it at least once every 3-6 months.
Rarely Restart Your Router
Like our bodies, electronics need regular breaks to function at full capacity. If you’re experiencing a slow connection, it may be your devices signaling to you that they need to rest. We recommend restarting your modem and router at least once a month to help troubleshoot any internet issues you may have. You can easily do this by setting a reminder on your phone or using an outlet timer to automatically reset plugged-in devices located at specific outlets.
Too Many Connected Devices
All devices on a single network – no matter if they’re wired or wireless – share a finite amount of bandwidth. Your WiFi router determines which devices need bandwidth and which devices use up the most, pulling randomly from each to ensure all devices have some form of connection. So, as you connect more devices to your network, you run the risk of overloading your network. This leads to latency issues and a poor user experience. To avoid this, make it a habit to disconnect devices throughout your house that are not currently being used. You can often see immediate results after decreasing your connected device count.
Not Enough Bandwidth
If disconnecting devices isn’t making a difference or isn’t an option with your lifestyle, it may be time to upgrade your internet plan to include faster speed. People often equate this to a provider’s poor service. However, different internet activities require different amounts of bandwidth, and no matter what you do, there’s always a limit depending on what you pay for. If this sounds like you, you may consider upgrading your internet plan to include higher internet speeds to fit your lifestyle. Make sure to factor in things like your family headcount, the number of devices typically connected, and how often the internet gets used when deciding which plan is right for you.
How to Speed Up Your Connection
In addition to the quick solutions above, here are a few tips for boosting your internet connection.
- Upgrade your internet equipment. Internet providers often supply their own equipment to access their service, but sometimes upgrading to high-quality products of your own can deliver better internet speeds.
- Invest in WiFi extenders. Strategically placed in areas of your home far from your router, WiFi extenders can extend your WiFi coverage to solve dead spot or buffering issues.
- Clear your browsing history. Make it a habit to delete your browser data at least once a month to make sure you’re not maxing out your bandwidth unnecessarily.
- Trade in old devices. Older devices typically cannot support faster networks, causing latency issues or no connectivity at all. Consider trading them in for store credit and upgrading to a new model.
- Upgrade your internet service. When all else fails, it may be time to listen to your lifestyle needs. Upgrading your internet plan to include a larger bandwidth will ultimately deliver the fastest speeds.
Internet Equipment
If you manage your internet connection at home, it’s good to have a general idea of how each piece of internet equipment works.
Modem
You can think of a modem as the gateway between your personal network and the open internet. It helps translate information and secure a connection between the two. Modems come either on their own or combined with your router in one device for an easier install. Either way, your modem needs to be hard-wired into your home for direct access to the internet.
Router
Similar to a modem, a wireless router helps secure a connection to the internet. However, rather than relying information to your home network, your router works as a switchboard that manages the connection between your devices and the internet.
Ethernet Cord
An ethernet cord is a network cable used to hard-wire your modem for access to the internet. It helps establish a more reliable and secure connection than WiFi, but it’s not as popular because it requires a person to be tethered to one area of the home.
Internet Speed Glossary
We really tried glossing over this one, but it never hurts to go back to the basics. To help you understand internet speed and how it all works, we’ve pulled together a glossary of the industry’s most used terms for you to have on hand.
- Bandwidth – This refers to the capacity of a particular internet connection, or in other words the fastest speed available at a given time to your network.
- Broadband – Internet connection is transmitted over many different frequencies, referred to as fiber, DSL, cable, and satellite. Broadband is used to describe any and all of this broad range of frequencies (bands).
- Bit – Internet speed is measured in bits per second (bps). Relayed in zeros and ones, a bit is the smallest unit of computer information and is the most common way ISPs refer to speeds in their internet plans.
- Byte – 1 byte equals 8 bits. Bytes are used to refer to how much memory is being transferred while using the internet and are occasionally used in advertised internet plans.
- Data Allowance – This is an allotted amount of data per month you’re able to use for your connected devices. Some internet providers use data allowances to regulate their networks and avoid congestion, however, other providers offer access to unlimited data.
- Download Speed – This is the measurement of how fast you can receive data from the internet to your connected device. Internet-based activities like streaming movies or scrolling through social media require download speeds to work properly.
- Internet – The internet is a massive network infrastructure connecting millions of computers around the world that allows for the transfer of data (information).
- Latency – Latency is the measurement of time it takes for data to transfer to its destination and back.
- Mbps – “Megabits per second” is how we gauge internet speed most of the time. This represents the bandwidth – or capacity – of an individual internet connection.
- MB (MBps) – “Megabytes per second” refers to file size in relation to how much data can be transferred each second.
- Modem – A modem is considered the gateway between your personal network and the world internet. This is hard-wired into your home for direct access.
- Ping – A ping is a test to confirm a connection to a network server. This test sends a data packet to the server to see if it comes back. If it does, a connection is active.
- Ping time – This measures how fasts a data packet travels to a server for testing and back. When it takes more than a few seconds, you will likely experience jitter in your connection.
- Router – A router is a device that communicates with your modem and acts as a switchboard for all the various devices connected to your network. Today, it’s common to rent or buy a router/modem combo.
- Upload Speed – This is a measure of how fast you can send data from your connected device to the internet. Internet-based activities like posting photos to your Facebook or uploading a file to the cloud require upload speeds to work.
- WiFi – A catchy phrase created to normalize the conception, WiFi refers to the connection we make from our devices to open networks using radio waves instead of hard lines.
Recap
Breaking down the basics, this Complete Guide to Understanding Your Internet Speed ultimately aims to improve any internet connection issues you may experience.
If you’re looking to switch internet providers or find better speed to fit your lifestyle, enter your zip code below to get started!
Find providers in your area

Table of Contents